Product Description
SAFElife T-Cup® 7 Panel CLIA Waived Instant Drug Test Cup, 25/Box
The T-Cup 7-Panel drug test detects the most commonly abused drugs and includes built-in Adulteration for Creatinine (CR), Specific Gravity (SG) and pH Level (PH). The One-Step cup is manufactured for accuracy, ease of use while maintaining competitive pricing. All T-Cup drug tests incorporate a Silicone Gasket "O" Ring in the cap to form a tight seal and prevent leakage.
T-Cup® Features
- CLIA Waived

- FDA 510(k) Cleared

- Health Canada Approved

- Built-In Adulteration Tests (S.V.T.)
- One-step, simple to use
- Easy-to-interpret color bands
- Versatile and easy-to-use
- Fast visible sample migration
- Up to 18 months shelf life on average
- Built in temperature strip
- Larger mouth design for easy use
- Reduced shipping costs with compact design
Order qualifies for free ground shipping!
| Seven Panel SAFElife™ T-Cup® Drug Test | ||
| Order Number | Panel Configuration | Approvals & Clearances |
| TDOA-274 | AMP, BZO, COC, mAMP, OPI, OXY, THC | FDA 510(k) K182701 CLIA Waived Health Canada License |
T-Cup® Results Interpretation
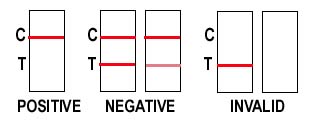
- Positive: A rose-pink band is visible in each (C) control region and NO color band appears in the appropriate (T) test region. It indicates a positive result for the corresponding drug of that specific test zone.
- Negative: A rose-pink band is visible in each control region and the appropriate (T) test region. It indicates that the concentration of the corresponding drug of that specific test zone is zero or below the detection limit of the test. The intensity of the color line is not a factor. Even a faint line indicates a negative result.
- Invalid test result: If a color band is not visible in the (C) control region or the color band is only visible in the (T) test region, the test result is invalid. Another test should be run to re-evaluate the specimen.
Optional Built-in Adulteration Detection - Configurations Listed Above
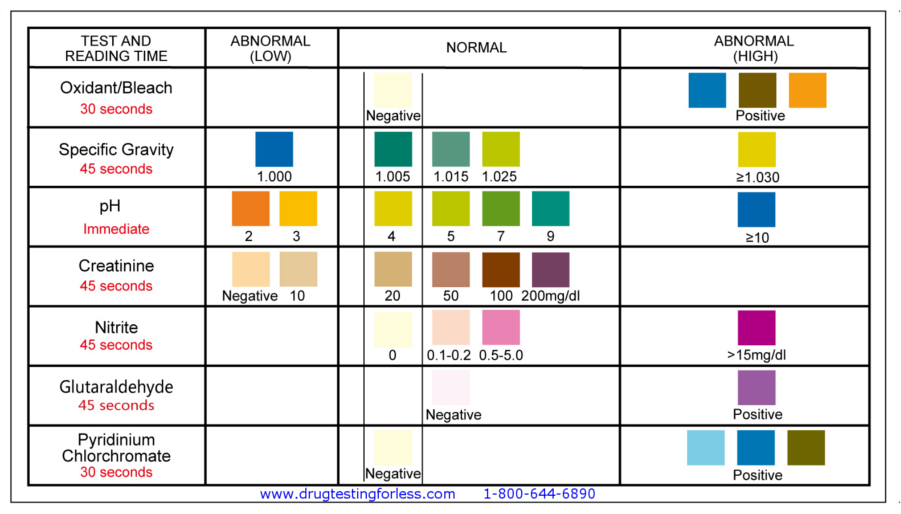
- Creatinine: Daily creatinine excretion, related to muscle mass of the human body, is usually constant. The DOT guideline states that urine specimens with creatinine levels of less than 20 mg/dl are indications of adulteration. Although these ranges are affected by age, sex, diet, muscle mass and local population distribution, sample with creatinine level of lower than 20 mg/dl should be considered adulterated.
- Glutaraldehyde: Glutaraldehyde is not a natural component of human urine and it should not be present in normal urine. The presence of glutaraldehyde in the urine sample indicates the possibility of adulteration. However, false positive may result when ketone bodies are , sample with creatinine levpresence in urine. Ketone bodies may appear in urine when a person is in ketoacidosis, starvation or other metabolic abnormalities.
- Nitrite: Although nitrite is not a normal component of urine, nitrite levels of up to 3.6 mg/dl may be found in some urine specimens due to urinary tract infections, bacterial contamination or improper storage. In this adulteration control, nitrite level above 7.5 mg/dl is considered abnormal.
- Oxidants: The presence of Bleach and other oxidizing reagents in the urine is indicative of adulteration since oxidizing reagents are not normal constituents of urine. Other oxidizing reagents include Hydrogen Peroxide, Ferricyanide, Persulfate, Pyridinium Chlorochromate…etc.
- pH: Normal urine pH ranges from 4.5 to 8.0. Values below pH 4.0 or above pH 9.0 are indicative of adulteration.
- Specific Gravity: Random urine may vary in specific gravity from 1.003 - 1.030. Normal adults with normal diets and normal fluid intake will have an average urine specific gravity of 1.016 - 1.022. Elevated urine specific gravity value may be obtained in the presence of moderate quantities of protein. DOT guidelines state that a urine specimen with specific gravity level of less than 1.003 is an indication of adulteration. Specific gravity and creatinine values should be considered together to provide a better picture of whether the sample is adulterated.
- Pyridium Chlorochromate: The presence of any chromate in urine is indicative of adulteration as chromate is not a normal constituent of urine.

- Temperature: Standard practice when collecting urine specimens for drug testing is to check the temperature of the specimen within four minutes of obtaining a viable specimen. Any temperature between 90 – 100 F is normal. Specimens with temperatures that are outside of this range are suspected of adulteration, substitution, or dilution.
Download & Print Reference Documents
![]() T-Cup Drug Test Package Insert
T-Cup Drug Test Package Insert
Additional Information
The CLIA Waived T-Cup urine drug detection test is ideal for testing employees, students or family members in private, medical offices, government, corporate, pain centers, healthcare facilities, and inmates in law enforcement facilities, probation situations, rehabilitation centers and clinics.
| T-Cup Drug Test Urine Panels | ||||
| Drug Panel | Abbreviation | Cutoff | Minimum Detection Time* | Maximum Detection Time* |
| Amphetamine | AMP | 1000 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 2-4 days |
| Barbiturates | BAR | 300 ng/ml | 2-4 hours | 1-3 weeks |
| Benzodiazepines | BZO | 300 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 1-4 days |
| Buprenorphine | BUP | 10 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 2-3 days |
| Cocaine | COC | 300 ng/ml | 1-4 hours | 2-4 days |
| Ecstasy | MDMA | 500 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 2-4 days |
| Marijuana | THC | 50 ng/ml | 2 hours | up to 40 days |
| Methadone | MTD | 300 ng/ml | 3-8 hours | 1-3 days |
| Methamphetamine | mAMP | 1000 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 2-4 days |
| Morphine | MOP / OPI-300 | 300 ng/ml | 2 hours | 2-3 days |
| Opiates | OPI | 2000 ng/ml | 2 hours | 2-3 days |
| Oxycodone | OXY | 100 ng/ml | 1-3 hours | 1-2 days |
| Phencyclidine | PCP | 25 ng/ml | 4-6 hours | 7-14 days |
| Tricyclic Antidepressants | TCA | 1000 ng/ml | 8-12 hours | 2-7 days |
| Propoxyphene | PPX | 300 ng/ml | 2-7 hours | 2-3 days |
| * Detection times are not guaranteed. This assay provides only a preliminary analytical test result. A more specific alternate chemical method must be used in order to obtain a confirmed analytical result. Gas Chromatography/Mass Spectrometry (GC/MS) is the preferred confirmatory method. Clinical consideration and professional judgment should be applied to any drug of abuse test result, particularly when preliminary positive results are indicated. | ||||






















